Human life on Earth is a rich tapestry woven by biology, culture, technology, and the environment. From the earliest times of foraging to contemporary urban civilizations, human ways of life have changed dramatically, compelled by innovation, social organizations, and the Earth’s varied ecosystems. This article examines how people live on Earth, their day-to-day lives, cultural traditions, technological progress, and relationship with the environment in 2025.
The Foundations of Human Life
Humans are biological beings, needing food, water, shelter, and air to live. These needs are the foundation of human ways of life everywhere. But the manner in which individuals fulfill these needs differs extensively depending on geography, economy, and culture.

Sustenance and Nutrition-HUMAN
Food is life and culture for human beings. Diet, in 2025, varies from plant foods in urban areas to hunting and gathering in isolated communities. Developed countries rely on industrial farming, vertical farming, and cultured meat proteins, but smallholder farming and foraging continue in rural and indigenous societies. Diets have diversified due to globalization, with cuisines merging across nations, but food insecurity is a problem in areas hit by conflict, climate change, or economic inequality.
Water availability also influences lifestyles. Sophisticated filtration units and desalination facilities make clean water readily available in most cities, yet in some regions, individuals continue to walk miles to retrieve water from wells or streams. Technologies such as atmospheric water generators are just starting to overcome shortages, yet fair distribution is a worldwide problem.

Shelter and Settlement in Human Life
Human settlements vary from vast megacities to nomadic camps. Urbanization keeps speeding up, with more than 60% of the world’s population residing in cities by 2025. Skyscrapers, intelligent homes, and green architecture are the hallmarks of urban environments, incorporating AI-based energy systems and sustainable materials. Rural and indigenous settlements, on the other hand, tend to use conventional building methods, employing local materials such as adobe, wood, or thatch.
Nomadic ways of life, while less prevalent, continue among the Central Asian Mongols or East African Maasai, who migrate with their flocks in synchrony with the cycles of the seasons. Such varied living patterns attest to mankind’s resilience against Earth’s diverse climes and landscapes.
Daily Routines and Work
The rhythm of human life is dictated by work, family, and leisure, though the balance varies across cultures and economic systems.
Work and Economy in Human Life
In 2025, the world’s workforce is a blend of old-school labor, gig economies, and virtual digital work. AI and automation have revolutionized industries, minimizing hands-on labor in factories but raising the need for technology-literate professionals. Virtual reality platforms and high-speed internet provide millions with the means to work together from home across continents. However, in less digitalized areas, agriculture, fishing, and traditional crafts are main sources of livelihood.
Economic inequalities have a profound impact on lifestyles. More affluent people get to enjoy state-of-the-art healthcare, education, and entertainment, whereas the poor tend to focus on survival rather than comfort. Some nations’ universal basic income trials try to close the gap, restructuring how individuals spend time between employment and leisure activities.

Family and Community in Human Life
Family organization is extremely diverse, ranging from nuclear families in Western countries to extended clans in some areas of Africa and Asia. Social ties are strengthened through meals shared together, celebrations, and ceremonies. Technology, and specifically social media and virtual communication, has reshaped community, facilitating worldwide connectivity at times at the expense of local bonds.
Cultural values are what child-rearing practices reflect. In some societies, children are brought up communally by villages, while others use digital media such as education apps or AI tutors. The commonality despite these differences is the universal desire to protect and care for the next generation.

Culture and Leisure
Culture shapes how humans express identity and find meaning. Art, music, religion, and storytelling are integral to human life, reflecting both individual and collective experiences.
Cultural Practices
Religious and spiritual practices continue to be a foundation of human existence. Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, Buddhism, and native belief systems inform moral structures and communal rituals. Secular philosophies such as humanism and environmentalism also shape contemporary lifestyles, especially in cities.
Festivals and celebrations, from Carnival to Diwali, unite people, combining age-old traditions with modern pizzazz. Language is also a cultural mainstay, with more than 7,000 languages spoken around the world, though technology is closing communication gaps.

Leisure and Technology
Free time is more and more influenced by technology. Streaming services, virtual reality games, and AI-created art are the focus of entertainment. Social media platforms such as X bring billions together, creating global discourse while prompting concerns over privacy and mental health.
Physical pursuits such as sports, hiking, and yoga continue in vogue, frequently touted as remedies to stationary city living. Tourism, facilitated by high-speed trains and electric planes, enables individuals to traverse Earth’s varying landscapes, but sustainable tourism becomes an increasing priority in the wake of climate-related concerns.

Interaction with the Environment
Human lifestyles are inseparable from the natural world. Earth’s ecosystems provide resources, but human activity has strained them, prompting shifts toward sustainability.
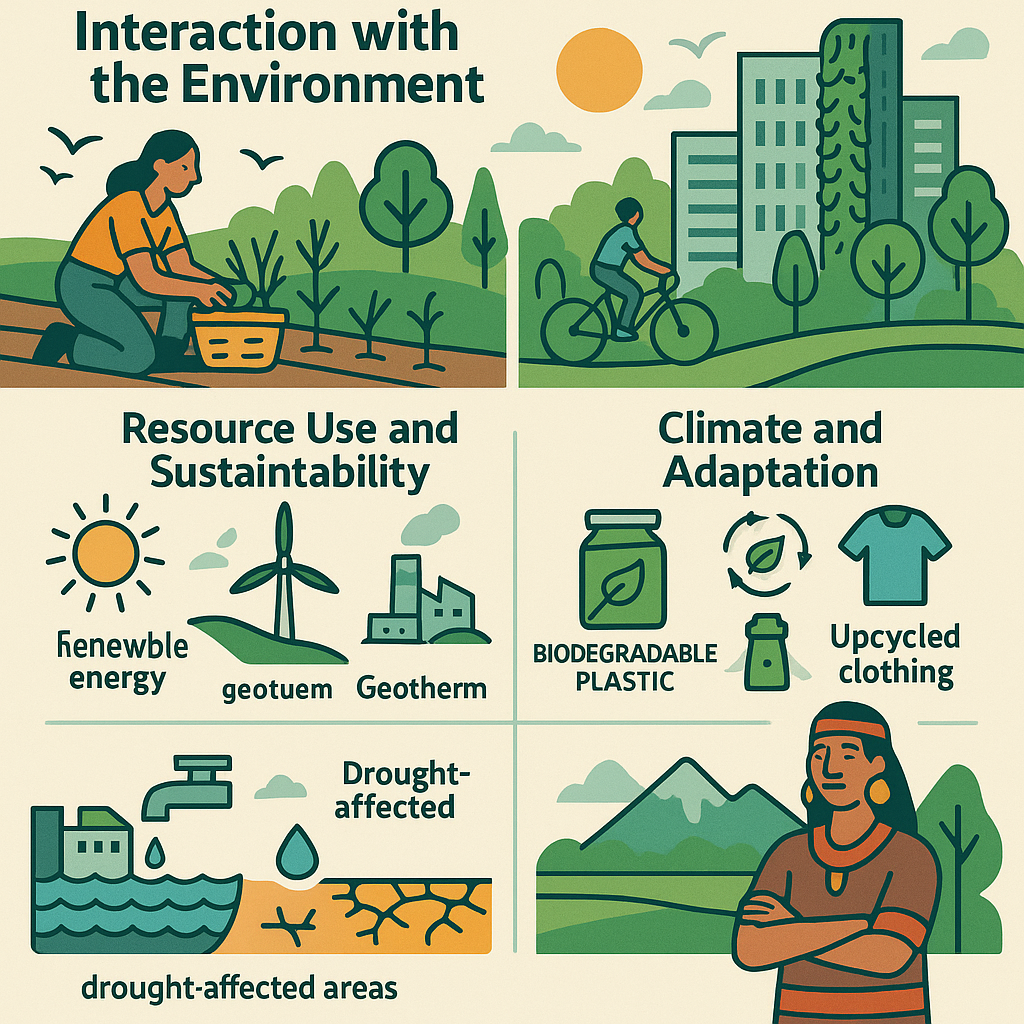
Resource Use and Sustainability
Energy use is a hallmark of contemporary life. Renewable energy such as solar, wind, and geothermal is supplanting fossil fuels in much of the world on the back of climate objectives. Circular economies with a focus on recycling and waste minimization are becoming popular, with innovations such as biodegradable plastics and upcycled clothing redefining consumption.
Urban design increasingly focuses on green spaces, with cities such as Singapore and Copenhagen incorporating vertical gardens and cycling infrastructure. Rural communities, on the other hand, tend to retain conventional knowledge of sustainable land use, such as crop rotation or agroforestry.
Climate and Adaptation
Human lives have been transformed by climate change, with increased temperatures, irregular weather, and sea-level rise compelling people to adapt. Coastal towns spend on flood protection, drought-affected areas implement water-saving technologies, and indigenous peoples, typically in the vanguard of climate change, combine traditional knowledge with new technologies to sustain their traditions.
Challenges and the Future
Notwithstanding progress, humankind is beset by issues that define day-to-day life. Inequality, political instability, and health crises challenge resilience. The COVID-19 pandemic, while predominantly brought under control by 2025, left profound effects on work, travel, and social mores. Awareness of mental health is growing, with mindfulness software and therapy becoming mainstream.
In the future, technology will continue to redefine human lives. Brain-computer interfaces, gene editing, and space travel may push the limits of what it means to be alive on Earth. However, the essence of human life—connection, creativity, and adaptation—will not change.
Conclusion
The human existence on planet Earth is a dynamic cycle of survival, culture, and innovation. From the urban jungles to the rural villages, humans adapt their surroundings using creativity and perseverance. As mankind confronts new challenges and opportunities, our ways of living will keep changing, illustrating our collective experience on this great planet.